Course objectives:
- Understand the basic principles of electronics:
- Understand basic concepts such as current, voltage, and resistance..
- Handling electronic components:
- Understand the role of components such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors..
- simple circuit design:
- Learn how to assemble and design simple electronic circuits..
- Reading electronic diagrams:
- Learn how to read and understand different electronic schematics..
- Use of measuring tools:
- Training on the use of measuring devices such as multimeters and oscilloscopes..
Electronics Basics Course: Detailed Content Explanation
1. Introduction to Electronics:
- Definition of electronics:Explain the scientific foundations of electronics and the difference between electricity and electronics.
- Electric current:The concept of electric current, its units, and types (direct current and alternating current).
- Electrical voltage:Definition of voltage and how to measure it, with practical examples.
- electrical resistance:Understand the concept of resistance, its units of measurement, and how it affects current.
2. Basic Laws:
- Ohm’s law:Explain the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance with practical applications.
- Kirchhoff’s laws:
- voltage law(KVL): Use in circuit analysis.
- Current law(KCL): Understanding current distribution in circuits.
- Electrical energy:Power consumption calculations in circuits.
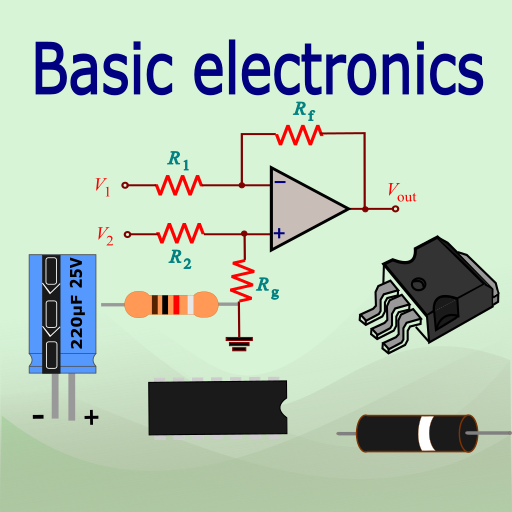
3. Basic electronic components:
- Resistors(Resistors):Its types, how to read it and use it in circuits.
- Capacitors(Capacitors):Its functions, types, and practical applications.
- Diodes(Diodes):How it works, its types, and its role in electric steering.
- Transistors(Transistors):Their types (BJT and MOSFET), and how to use them as switches and amplifiers.
4. Analog and digital circuits:
- Analog circuits:How it works, examples such as amplifier circuits.
- Digital circuits:Learn about basic logic gates (AND, OR, NOT) and their applications in digital circuits.
5. Circuit design and installation:
- Initial planning:How to draw electronic schematics using component symbols.
- Circuit assembly:Steps for assembling circuits on breadboards.
- Practical project:Design a simple circuit such as an LED light operated by a switch.
6. Electrical Safety:
- Safety principles:The importance of taking safety measures when working with circuits.
- Practical precautions:How to handle electrical appliances and tools to avoid accidents.
7. Use of measuring tools:
- Multimeter(Multimeter):How to use it to measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Oscilloscope(Oscilloscope):Use it to monitor electrical signals and understand waveforms.
-
- .
Target group:
- Those interested in entering the field of electronics.
- Engineering and Electronics Students.
- Hobbyists who want to develop their knowledge of electronics.